Introduction
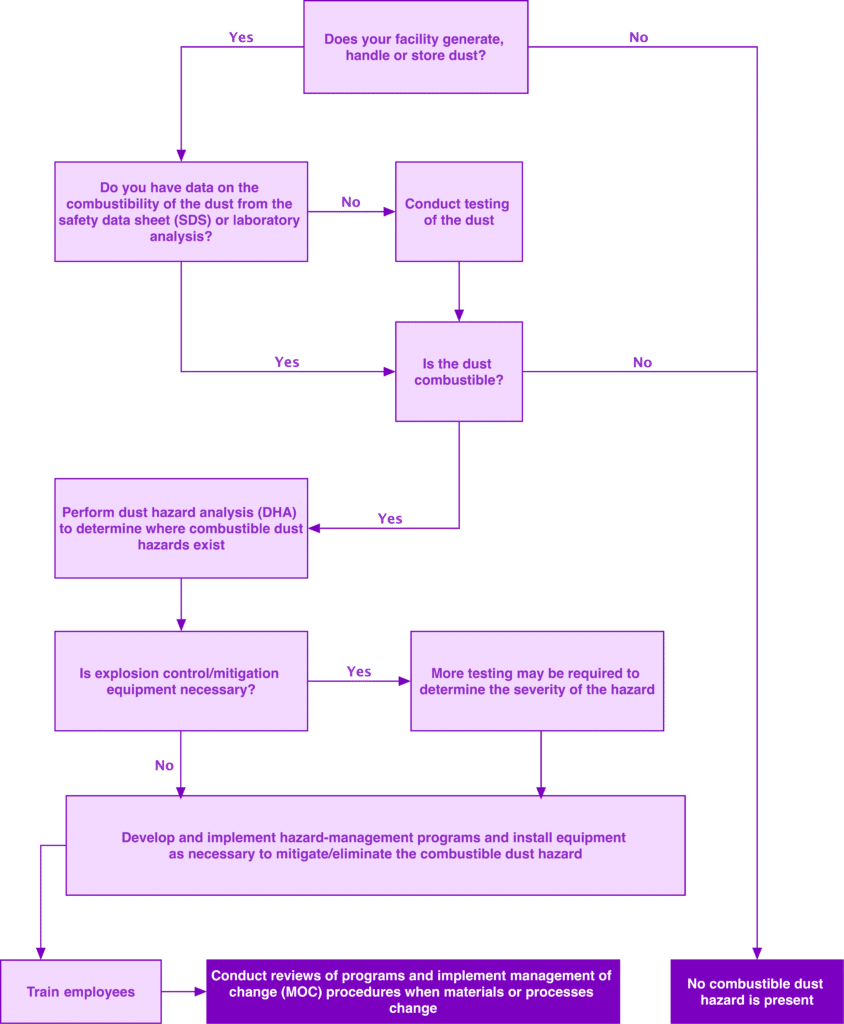
A Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA) clearly outlines the systematic process of identifying, evaluating, and managing the risks associated with combustible dust. This analysis is especially critical for facilities that handle, process, or store combustible bulk solids, as it helps prevent fires, flash fires (deflagrations), and explosions. By selecting and applying the right dust hazard analysis method, facilities can implement protective measures tailored to their specific operations and risks. Moreover, a well-executed DHA not only reduces the chance of catastrophic incidents but also helps safeguard employees, equipment, and the overall supply chain.
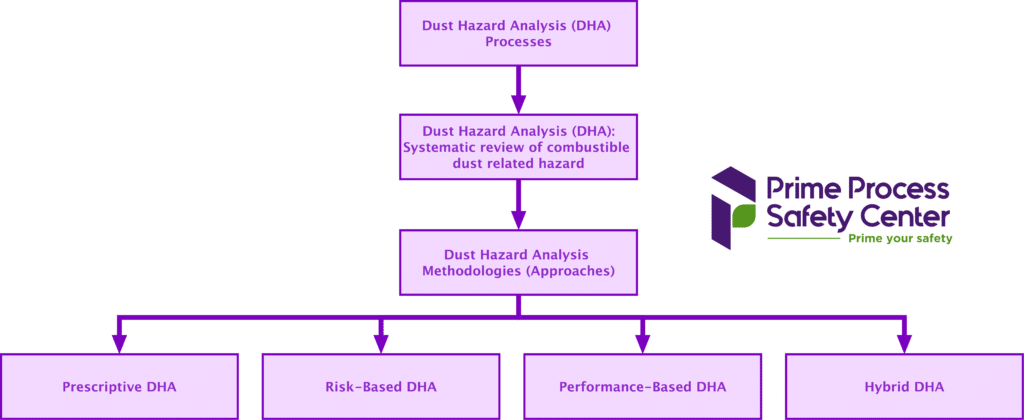
When it comes to choosing the appropriate dust hazard analysis method, it depends largely on the facility’s unique conditions and applicable regulations. Each method, therefore, is designed to meet specific safety goals and align with industry standards. Common types include:
- Prescriptive Based Dust Hazard Analysis
- Risk-Based Dust Hazard Analysis
- Performance-Based Dust Hazard Analysis
- Hybrid Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA)
Prescriptive Based Dust Hazard Analysis
A Prescriptive-Based Dust Hazard Analysis, by design, follows established guidelines and standards to systematically evaluate and mitigate combustible dust hazards in industrial environments. Through this structured approach, analysts rely on predetermined criteria to consistently identify potential hazards and then implement corresponding preventive measures. Typically, the process includes the following key steps:
- Gathering facility information
- Identifying applicable regulations
- Evaluating dust characteristics
- Reviewing building and equipment with controls
- Developing prevention and mitigation measures
- Documenting findings and recommendations
By following these steps, organizations can proactively mitigate risks and maintain safety standards.
Advantages:
-
Clear Guidelines: Provides structured steps aligned with regulatory standards.
-
Time Efficiency: Saves time by using predefined protocols, helpful for facilities with limited resources.
-
Consistency: Ensures a standardized approach across different sites or teams.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Helps demonstrate adherence to industry regulations.
-
Industry Acceptance: Based on well-recognized standards, enhancing credibility with stakeholders.
Disadvantages:
-
Limited Flexibility: May not accommodate unique or complex processes.
-
Risk of Overlooked Hazards: Prescriptive methods may miss facility-specific issues.
-
False Sense of Security: Compliance doesn’t always equal comprehensive safety.
-
Limited Innovation: Rigid guidelines can inhibit new, more effective safety strategies.
-
Complex Implementation: May still require specialized training for accurate application.
Risk-Based Dust Hazard Analysis
A Risk-Based Dust Hazard Analysis (RB-DHA) moves beyond rigid standards to assess facility-specific hazards and their potential consequences. It starts with identifying dust-related risks—such as ignition sources and dust accumulation—while also evaluating variables like particle size, moisture content, and chemical composition. Once these hazards are identified, a thorough risk assessment follows, often incorporating historical data and expert judgment to better prioritize mitigation efforts based on likelihood and severity.
Importantly, consequence analysis plays a key role, examining potential impacts on personnel, structures, and the environment. With these insights in hand, organizations can then develop risk mitigation strategies, including engineering controls, administrative procedures, and PPE. Finally, ongoing review and monitoring are essential to ensure continued effectiveness and to adapt to any changes in processes or materials over time.
Advantages:
-
Customized Approach: Tailored to the facility’s unique characteristics.
-
Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Evaluates all relevant factors beyond prescriptive requirements.
-
Prioritized Risk Management: Helps allocate resources based on greatest need.
-
Flexibility: Adapts to changes in processes, technology, and regulations.
-
Continuous Improvement: Encourages regular updates and proactive safety management.
Disadvantages:
-
Subjectivity: Judgments can vary between assessors.
-
Complexity: Requires significant technical knowledge.
-
Resource Intensive: Demands time, data, and expertise.
-
Data Availability: Effectiveness depends on access to accurate, detailed information.
-
Compliance Challenges: Must still align with applicable regulations.
Performance-Based Dust Hazard Analysis
A Performance-Based Dust Hazard Analysis (PB-DHA) emphasizes achieving safety outcomes based on specific facility goals rather than simply following standard checklists. The process begins by defining safety performance objectives—such as controlling dust concentrations, preventing ignition, and ensuring personnel protection.
Hazard scenarios are analyzed in light of these goals, and existing safeguards are measured against performance criteria. Any gaps identified lead to customized mitigation strategies, including engineering upgrades, procedural improvements, and training. Ongoing evaluation ensures continuous alignment with safety targets.
Advantages:
-
Customization: Tailored to the facility’s operations, risk tolerance, and safety culture.
-
Flexibility: Encourages innovative solutions beyond regulatory minimums.
-
Performance Focus: Targets specific safety outcomes instead of compliance alone.
-
Continuous Improvement: Regular reviews lead to progressive enhancements.
-
Holistic Risk Management: Considers organizational, operational, and technical factors.
Disadvantages:
-
Complexity: May be difficult for organizations with limited experience or resources.
-
Subjectivity: Performance goals and evaluation criteria can vary between stakeholders.
-
Data Requirements: Relies on high-quality, comprehensive information.
-
Regulatory Balancing: Must still comply with relevant codes and standards.
-
Measurement Challenges: Defining and verifying success can be difficult.
Hybrid Dust Hazard Analysis
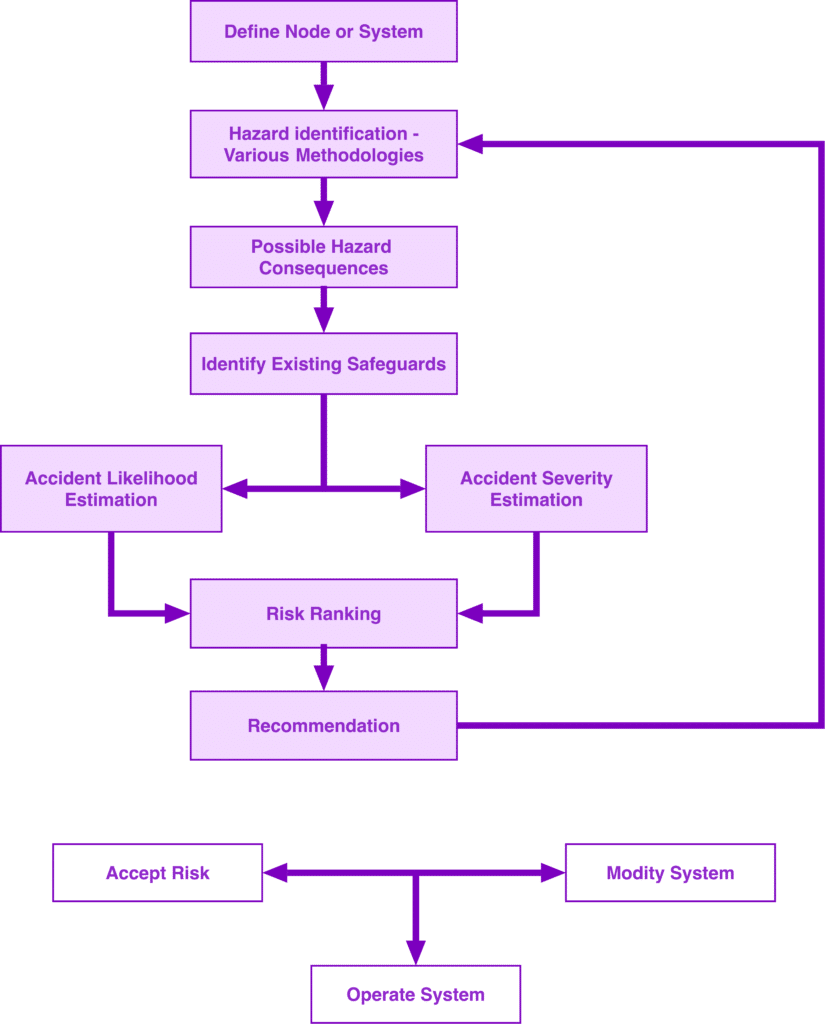
A Hybrid Dust Hazard Analysis (HDHA) combines prescriptive, risk-based, and performance-based methods to thoroughly evaluate and mitigate combustible dust hazards in industrial environments. It begins with meticulous hazard identification, integrating prescriptive guidelines, historical data, and expert insights to capture all potential risks. Next, a comprehensive risk assessment uses both qualitative and quantitative techniques to prioritize hazards based on severity and likelihood, aligning with risk-based analysis principles for efficient resource allocation.
In parallel, performance-based criteria are developed and used to evaluate existing controls, identify gaps, and guide targeted improvements. Based on these findings, tailored mitigation strategies are implemented, blending engineering controls, administrative procedures, training, and equipment updates. Following implementation, ongoing monitoring and periodic reviews ensure these strategies remain effective amid changes in processes, regulations, or best practices.
Moreover, thorough documentation and communication with stakeholders promote transparency and accountability throughout the DHA process. By integrating diverse analytical methods, the hybrid approach strengthens workplace safety and reduces the risk of dust-related incidents. The figure below outlines a typical hybrid DHA framework, incorporating both qualitative and quantitative steps.
Advantages:
-
Integration of Approaches: Leverages strengths from all three methodologies.
-
Customization and Flexibility: Adapts to the facility’s unique needs.
-
Holistic Risk Management: Captures a wide range of hazard types.
-
Balanced Strategy: Aligns compliance with performance-driven improvements.
-
Supports Continuous Improvement: Encourages iterative evaluation and upgrades.
Disadvantages:
-
Complex and Resource Intensive: Can be demanding to implement and maintain.
-
Subjectivity and Interpretation: May lead to differences in priorities or solutions.
-
High Data Requirements: Effectiveness depends on availability and accuracy of data.
Cost Considerations When Selecting a DHA Methodology
While each Dust Hazard Analysis methodology has technical merits, cost and resource requirements often influence which approach is selected. Industry experience has shown that prescriptive DHAs generally require lower upfront effort, while risk-based and performance-based DHAs demand significantly more time, data, and engineering analysis. For facilities with complex processes or unique equipment, these advanced approaches may be justified, but they are not always necessary at a facility-wide level.
Extensive industry practice has demonstrated that a cost-effective DHA strategy often combines multiple methodologies. In this approach, a prescriptive DHA is used to evaluate the overall facility, ensuring broad hazard identification and alignment with recognized standards. Risk-based or performance-based analyses are then applied selectively to specific equipment or processes where strict prescriptive compliance may be impractical or unnecessary. This targeted use of advanced methodologies allows facilities to justify alternative safeguards without incurring the high cost of applying complex analyses across the entire facility.
Conclusion
Conducting a Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA) is a critical step in identifying and managing the fire and explosion risks associated with combustible dust. For industries that generate, handle, or store combustible dust, a DHA provides a structured way to understand where hazards exist, how they can develop, and which safeguards are necessary to control risk effectively.
Selecting the appropriate DHA methodology allows facilities to evaluate explosion potential, assess the adequacy of existing controls, and justify additional protective measures where needed. When applied correctly, a DHA supports safer operations, protects equipment, minimizes unplanned downtime, and improves overall process reliability. Rather than serving only as a compliance exercise, a well-executed DHA methodology functions as a proactive risk management tool that strengthens long-term industrial safety and operational performance.