What is Process Safety Management (PSM)?
PSM is a regulatory framework designed to prevent the release of hazardous chemicals that could cause serious harm to workers and the public. Process Safety Management (PSM) is a systematic approach to managing the risks associated with highly hazardous processes in various industries, with a primary focus on preventing catastrophic incidents, such as chemical explosions, fires, releases of toxic substances, and other process-related accidents. PSM is particularly relevant to industries such as chemical manufacturing, petrochemicals, oil and gas production, refineries, and other facilities where hazardous chemicals or processes are involved. The PSM program is required in the United States under the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standard 29 CFR 1910.119. Other countries and regions have their own regulations and standards that may be similar in nature. The primary goal of PSM is to prevent accidents and incidents, protect personnel and the environment, and ensure the safe operation of highly hazardous processes. It helps organizations systematically manage the complex risks associated with these processes and maintain a strong commitment to safety.
Why implement Process Safety Management (PSM)?
Performing Process Safety Management (PSM) is crucial for effectively controlling hazards associated with the handling, processing, and storage of hazardous chemicals. PSM is integral to preventing industrial accidents such as fires, explosions, and toxic releases, which pose significant risks to human life, the environment, and property. Its implementation ensures a systematic approach to identifying potential hazards, assessing risks, and implementing appropriate safety measures. This not only safeguards the workforce and the community but also upholds operational integrity and business continuity. Compliance with PSM regulations, such as those mandated by OSHA, is not only a legal requirement but also a reflection of an organization’s commitment to maintaining high safety standards. Furthermore, PSM fosters a proactive safety culture within organizations, encouraging continuous improvement and diligent risk management practices, which are essential for the sustainable and responsible operation of any facility handling hazardous materials.
What are the regulatory requirements for Process Safety Management (PSM)?
The regulatory requirements for Process Safety Management (PSM) primarily stem from the standards set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, specifically in the OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.119. This standard is designed to prevent or minimize the consequences of catastrophic releases of toxic, reactive, flammable, or explosive chemicals. These requirements apply to industries that deal with hazardous chemicals, including but not limited to petroleum refineries, chemical plants, and other industrial facilities.
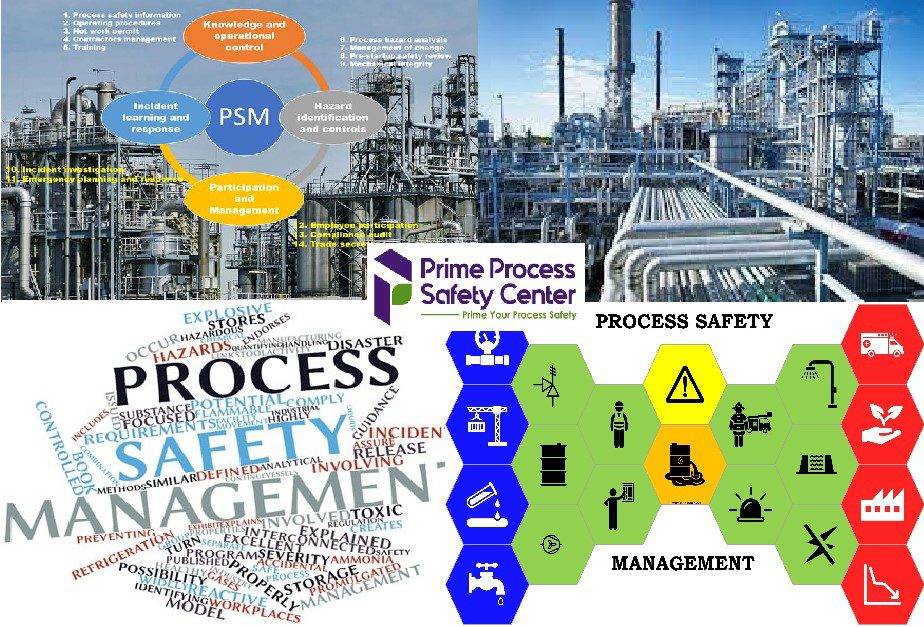
What are the elements of Process Safety Management (PSM)
- Employee Participation: Involving employees in the development and implementation of PSM programs.
- Process Safety Information (PSI): Compiling detailed information about the chemicals, technology, and equipment used in the processes.
- Process Hazard Analysis (PHA): Conducting systematic assessments to identify, evaluate, and control hazards associated with processes.
- Operating Procedures: Developing and maintaining written instructions for safely conducting activities involved in the process.
- Training: Ensuring employees are trained in operating procedures and emergency response to perform their duties safely.
- Contractors: Ensuring that contractors are informed about potential hazards and that their work practices comply with PSM standards.
- Pre-startup Safety Review (PSSR): Conducting reviews before starting new or modified processes to ensure safety systems are in place and functional.
- Mechanical Integrity: Ensuring that critical equipment is properly designed, installed, maintained, and inspected to prevent failures.
- Hot Work Permits: Requiring written authorization for hot work activities such as welding and cutting to prevent ignition of flammable materials.
- Management of Change (MOC): Implementing a systematic approach to managing alterations to process chemicals, technology, equipment, and procedures.
- Incident Investigation: Investigating incidents that resulted in or could have resulted in catastrophic releases of hazardous chemicals to identify root causes and prevent recurrence.
- Emergency Planning and Response: Developing and implementing plans to respond effectively to process-related emergencies to protect workers and the community.
- Compliance Audits: Conducting regular audits to ensure adherence to PSM requirements and evaluate the effectiveness of the PSM program.
- Trade Secrets: Managing confidential business information while ensuring necessary disclosure to employees and contractors for safety purposes.
Why is PSM important?
PSM is essential to prevent accidents such as fires, explosions, and toxic releases, ensuring the safety of workers, the public, and the environment.
What regulations govern PSM in the United States?
In the U.S., PSM is governed by OSHA’s standard 29 CFR 1910.119 and the EPA’s Risk Management Plan (RMP) Rule.
What are the key elements of PSM?
The key elements include employee participation, process safety information, process hazard analysis, operating procedures, training, contractors, pre-startup safety review, mechanical integrity, hot work permits, management of change, incident investigation, emergency planning and response, compliance audits, and trade secrets.
What is a Process Hazard Analysis (PHA)?
A PHA is a systematic assessment of potential hazards associated with industrial processes to identify and analyze the significance of risks.
How often must a PHA be updated?
A PHA must be updated and revalidated at least every five years.
What is process safety information (PSI)?
PSI includes detailed information on the chemicals, technology, and equipment involved in processes, which is necessary for understanding and managing process safety.
What is the role of employee participation in PSM?
Employees must be involved in all aspects of PSM, including PHAs and incident investigations, to ensure their insights and knowledge contribute to process safety.
What are operating procedures in PSM?
Operating procedures are detailed, written instructions for safely conducting activities involved in the process, ensuring consistency and safety.
How is training related to PSM?
Employees must be trained in operating procedures, emergency response, and process safety principles to ensure they understand how to safely perform their duties.
What is the significance of mechanical integrity in PSM?
Mechanical integrity ensures that critical equipment is designed, installed, maintained, and inspected properly to prevent failures that could lead to hazardous releases.
What is a management of change (MOC) process?
MOC is a systematic approach to managing alterations to process chemicals, technology, equipment, and procedures to ensure that changes do not introduce new hazards.
What is a pre-startup safety review (PSSR)?
PSSR is a thorough review conducted before starting new or modified processes to ensure all safety systems are in place and functional.
Why are incident investigations important in PSM?
Incident investigations identify root causes of process incidents to prevent recurrence and improve safety practices.
What is emergency planning and response in PSM?
This involves developing and implementing plans to respond effectively to process-related emergencies, protecting workers and the community.
How often must compliance audits be conducted in PSM?
Compliance audits must be conducted at least every three years to ensure adherence to PSM requirements.
What is the role of contractors in PSM?
Contractors must be trained and informed about potential hazards, and their work practices must comply with PSM standards to ensure safety.
What is a hot work permit?
A hot work permit is a written authorization required for activities that could ignite flammable materials, such as welding or cutting.
What are trade secrets in the context of PSM?
Trade secrets are confidential business information that must be disclosed to employees and contractors as needed to ensure process safety, while protecting proprietary information.
How does PSM address process safety culture?
PSM promotes a safety culture by involving employees in safety processes, encouraging reporting of safety concerns, and ensuring management commitment to safety.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with PSM regulations?
Consequences include fines, legal action, increased risk of accidents, and damage to the company’s reputation.
What is the purpose of a PSM compliance audit?
A PSM compliance audit evaluates the effectiveness of the PSM program and ensures all regulatory requirements are being met.
How can technology improve PSM?
Technology can enhance PSM through improved data management, real-time monitoring, advanced modeling, and predictive analytics for better hazard identification and control.
What are some common challenges in implementing PSM?
Challenges include maintaining up-to-date process safety information, ensuring effective employee training, managing changes, and sustaining management commitment.
What role does leadership play in PSM?
Leadership is crucial for establishing a strong safety culture, providing resources, and ensuring continuous improvement in process safety practices.
How is PSM integrated with other safety management systems?
PSM can be integrated with systems like occupational safety, environmental management, and quality management to create a comprehensive safety approach.
What are some examples of process safety incidents?
Examples include the Bhopal gas tragedy, the Texas City refinery explosion, and the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, all of which highlight the importance of effective PSM.
What is a Risk Management Plan (RMP)?
An RMP is a detailed plan required by the EPA that outlines measures for preventing and responding to chemical accidents, including hazard assessment, prevention programs, and emergency response plans.
How does PSM address human factors?
PSM considers human factors by addressing ergonomics, human error potential, operator training, and workload management to enhance safety and performance.
What is the future of PSM?
The future of PSM includes increased use of digital tools, advanced analytics, and a stronger focus on safety culture and human factors to further reduce the risk of process incidents.
What services does Prime Process Safety Center offer?
Prime Process Safety Center offers the following Combustible Dust Consulting Services; Combustible Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA), Ignition Sources Assessment, Electrostatic Hazard Assessment, Hazardous Area Classification, Fire and Explosion Hazard Analysis, Explosion Prevention and Protection Consulting Services, Fire and Building Code Services, Incident Investigation, Expert Witness and Litigation, Process Safety Management (PSM), Process Safety Management (PSM) Gap Analysis, Process Safety Management Compliance Review and Audit and Hazard Identification and
Moreover, Prime Process Safety Center offers the following combustible dust testing services Go/No Go Explosibility Screening, Burn Rate / Fire Train Test, Dust Explosion Severity (Kst/Pmax/dP/dt), Minimum Explosible Concentration (MEC)/Lower Explosible Limit (LEL), Limiting Oxygen Concentration (LOC) Test, Minimum Ignition Energy (MIE), Minimum Autoignition Temperature-Cloud (MAIT – Cloud), Layer Ignition Temperature of Dust (LIT), Volume Resistivity, Surface Resistivity, Charge Decay (Relaxation) Time, Breakdown Voltage, Flexible Intermediate Bulk Containers (FIBC), Electrostatic Chargeability Testing, Basket Self-Heating, Grewer Oven Test, Air Over Layer/Powder Layer Test, Bulk Powder Test, Aerated Powder Test


Everything is very open with a clear clarification of
the challenges. It was truly informative. Your website is extremely helpful.
Many thanks for sharing!
A person essentially assist to make seriously posts I would state.
This is the first time I frequented your website page and
up to now? I surprised with the analysis you made to create this particular put up extraordinary.
Magnificent task!
I am not sure where you’re getting your information, but good topic.
I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more.
Thanks for excellent info I was looking for this information for my mission.
What’s up, of course this post is actually nice and I have learned lot of things from it about
blogging. thanks.