We also offer
What Is a Layer Ignition Temperature of Dust (LIT) Test?
The Layer Ignition Temperature (LIT), also known as the Minimum Ignition Temperature (MIT) of a dust layer, is the lowest temperature at which a dust layer can autoignite on a hot surface. This test helps determine the maximum safe operating temperature for electrical and non-electrical equipment in environments where combustible dust may accumulate.
Testing Principle and Methodology
To determine the LIT:
-
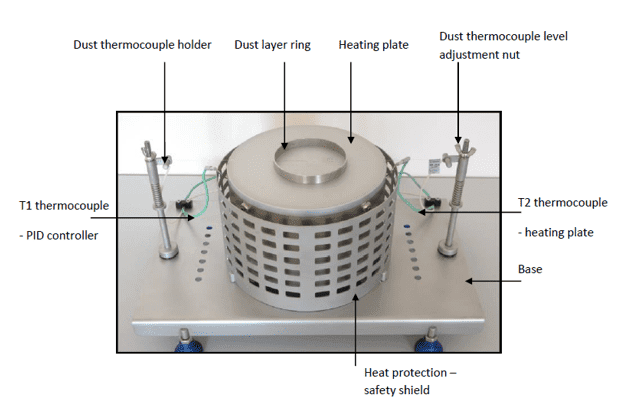
A 12.7 mm thick layer of the sample is placed on a preheated hot surface.
-
A K-type thermocouple is positioned across the surface of the sample to monitor temperature changes.
-
The surface temperature is held constant, and the sample is observed for up to 2 hours.
Ignition is defined by any of the following:
-
Visible flame or glow (incandescence)
-
A rise in the material’s temperature of at least 50°C above the hot surface temperature
If ignition occurs, the test is repeated with a fresh sample at a lower surface temperature until ignition no longer happens. At that point, the LIT value is established.
ASTM recommends:
-
Particle size: 95% of the material should be <75 microns
-
Moisture content: <5%
In unique cases where material segregation is unlikely, the sample can be tested as received. For clarification, contact Prime Process Safety Center.
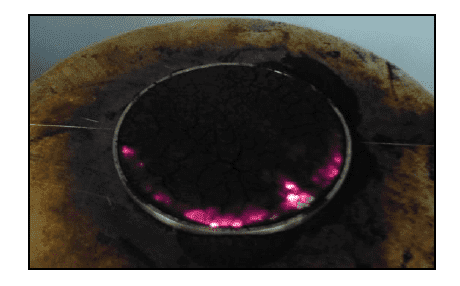
Dust Layer Igniting on a Hot surface
Applicable Standard
This test follows ASTM E2021, Standard Test Method for Hot-Surface Ignition Temperature of Dust Layers.
Data Interpretation
-
Common LIT values: Between 300°C and 400°C for most organic solids and some metal powders.
-
Sensitive materials: Some dusts like Lycopodium powder can have LIT values below 250°C.
The LIT test helps:
-
Evaluate the risk of ignition from hot surfaces
-
Guide the selection of equipment for Class II locations
-
Inform safe handling and storage conditions for combustible dust
When to Perform a Layer Ignition Temperature Test?
You should perform an LIT test when:
-
Evaluating the risk of hot surface ignition during powder handling
-
Working with materials prone to accumulate in dust layers
-
Designing safety protocols to prevent fires from combustible dust layers
Why Choose Prime Process Safety Center
At Prime Process Safety Center:
-
We bring deep expertise in process safety testing
-
Our lab operates with state-of-the-art LIT testing equipment
-
We follow strict testing protocols for precision and consistency
-
Our experienced team provides clear data interpretation and tailored recommendations for your operations
- As an ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accredited laboratory, we uphold rigorous quality and competency standards in every test we perform
Our goal is to deliver accurate, reliable, and defensible results that comply with industry and regulatory standards.
FAQ
What is the Layer Ignition Temperature (LIT) of a dust layer?
Answer: The LIT of a dust layer refers to the lowest temperature at which a layer of combustible dust can self-ignite and sustain combustion without an external ignition source.
Why is the LIT of a dust layer important in industry?
Answer: Knowing the LIT is crucial for assessing fire hazards associated with combustible dust layers. It aids in establishing safe storage, handling practices, and preventive measures in industries to mitigate fire risks.
How is the LIT of a dust layer determined?
Answer: Determining the LIT involves specialized testing where dust layers are subjected to increasing temperatures until ignition occurs, observing the lowest temperature at which self-ignition happens.
What factors influence the LIT of a dust layer?
Answer: Factors such as dust composition, particle size, moisture content, and specific characteristics of the dust significantly impact the MIT.
How does the LIT vary among different types of combustible dust?
Answer: Different types of dust have varying MITs based on their inherent properties. Finer particles, higher moisture content, or certain chemical compositions can affect MIT values.
What safety measures should be implemented based on the LIT of a dust layer?
Answer: LIT data aids in establishing safety guidelines, including safe temperature thresholds for storage, handling, and operational controls to prevent spontaneous ignition.
How do environmental conditions affect the LIT of a dust layer?
Answer: Factors like temperature, humidity, and airflow influence the LIT. Higher temperatures or dry conditions might decrease the LIT.
Does the LIT change over time for stored dust layers?
Answer: Aging, contamination, or changes in dust properties might impact the LIT over time, requiring periodic reassessment of safety measures.
In what industries or scenarios is knowledge of the LIT of a dust layer crucial?
Answer: Industries dealing with combustible dust, such as woodworking, food processing, or pharmaceuticals, find LIT data essential for fire prevention and workplace safety.