We also offer
What Is Electrical Surface Resistivity?
Electrical surface resistivity is the electrical resistance of the surface of a material, expressed in Ohms per Square (Ω/sq). It is independent of the material’s size or thickness. Surface resistivity is calculated based on the surface resistance of the material and the known geometry of the electrodes. It represents the material’s resistance to current flow when an electrical potential difference is applied across its surface. Unlike volume resistivity, surface resistivity specifically addresses the electrical characteristics of a material’s surface layer, affecting its behavior in applications such as coatings, films, and insulating layers. Surface resistivity measurements are a key part of Electrostatics Testing, especially for evaluating how materials respond to electrical charge buildup.
Factors influencing surface resistivity include material composition, surface treatments, moisture, temperature, contamination, and mechanical stress. These factors impact the surface’s conductivity or insulation properties.
Testing Principle and Methodology
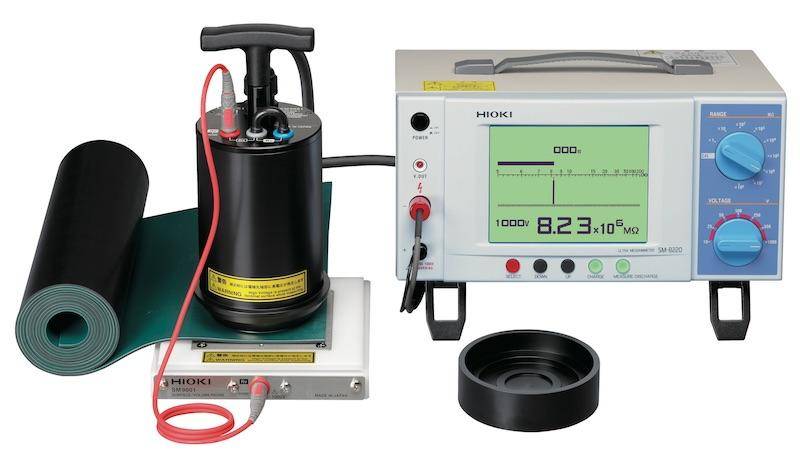
Place two electrodes of equal length on the material’s surface, spaced at a known distance. Apply a direct current voltage to one electrode and measure the resulting current at the other. Alternatively, you can use a concentric test cell with a known cell constant. Use a megger-ohmmeter to measure the resistance directly. Then, calculate the surface resistivity using the formula:
Where:
-
ρ = Resistivity in ohms per square (Ω/sq)
-
R = Measured resistance
-
= Length of electrode
-
= Distance between electrodes
Testing is typically conducted on solid materials in their commercial form and under varying humidity conditions.
Factors such as temperature, relative humidity, and surface cleanliness can affect measurement accuracy. It is critical to ensure the surface is clean and free from contamination to avoid skewed results.
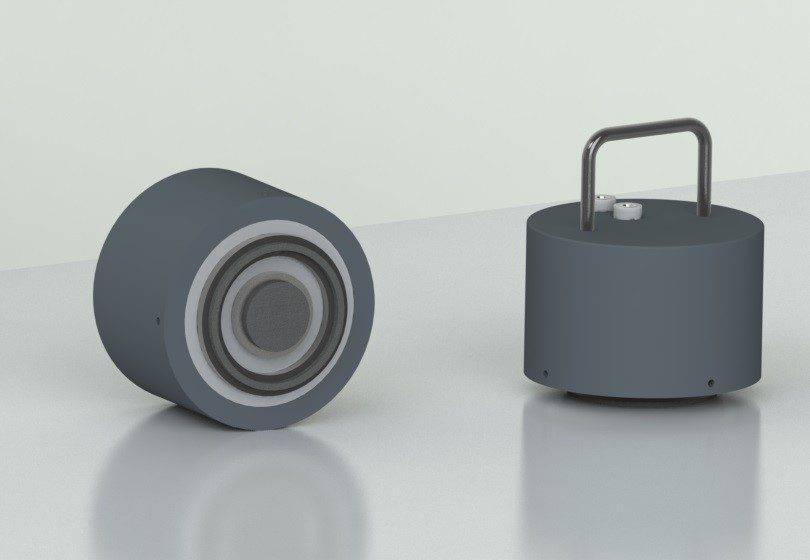
Surface Resistivity Test Electrode manufactured by ANKO.
Applicable Standard
Surface resistivity testing is performed according to these standards:
-
ASTM D257: Standard Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
-
BS 5958: Part 1: 1991
-
BS 7506: Part 2: 1996
-
NFPA 77
Data Interpretation
Surface resistivity values are classified as follows:
| < 10⁵ | Conductive / Low Resistivity |
| 10⁵ to 10⁹ | Static Dissipative / Medium Resistivity |
| > 10⁹ | Non-Conductive / High Resistivity |
Knowing your material’s surface resistivity enables safe handling measures. Materials should be handled in a well-earthed environment to prevent electrostatic charge buildup. Sudden discharge of accumulated charge can ignite flammable atmospheres, so understanding electrostatic properties is crucial to preventing such hazards.
When to Perform Surface Resistivity Testing
Surface resistivity testing is recommended for liners, laminates, and sheets used in applications such as personal protective equipment (PPE), where controlling electrostatic charge accumulation is critical. Generally, higher surface resistivity indicates a more resistive, less conductive material that tends to accumulate and retain charges. Materials with low resistivity or static dissipative properties more readily conduct or dissipate charge.
Why Choose Prime Process Safety Center
Prime Process Safety Center is a leader in process safety testing with experienced laboratory personnel dedicated to delivering accurate, reliable, and defensible data that meets industry and regulatory standards.
-
We specialize in surface resistivity testing, ensuring precise and reliable results.
-
Our state-of-the-art equipment offers sensitive, accurate measurements.
-
We follow strict testing protocols and quality control to maintain consistency.
-
Our experts analyze and interpret your data, providing valuable insights tailored to your application or research.
- As an ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accredited laboratory, we follow rigorous quality and competency requirements for every test we perform.
FAQ
What is Surface Resistivity?
Answer: Surface resistivity is the measure of a material's ability to resist or conduct electrical current across its surface when an electrical potential difference is applied.
How is Surface Resistivity Different from Volume Resistivity?
Answer: Surface resistivity refers to the resistance along the surface area, while volume resistivity is the resistance through the volume of a material. Surface resistivity deals specifically with the material's surface conductive properties.
What Units are Used to Express Surface Resistivity?
Answer: Surface resistivity is commonly expressed in ohms per square (Ω/sq), representing the resistance between two opposite edges of a square sample of the material.
Why is Surface Resistivity Important?
Answer: Surface resistivity is crucial for assessing a material's suitability for electrical insulation, static dissipation, and determining its conductive or insulative properties on the surface.
How is Surface Resistivity Testing Performed?
Answer: Surface resistivity testing involves applying a known voltage across the material's surface and measuring the resulting current to calculate the resistance. The resistance and electrodes’ length and distance determine the surface resistivity.
What Factors Influence Surface Resistivity?
Answer: Material composition, surface treatments, temperature, moisture content, contaminants, and environmental conditions affect surface resistivity.
What Materials Have High Surface Resistivity?
Answer: Insulating materials such as ceramics, glass, and certain plastics often exhibit higher surface resistivity, making them suitable for electrical insulation purposes.
Where is Surface Resistivity Testing Applied?
Answer: Surface resistivity testing is used in various industries for selecting materials in electronics, manufacturing of antistatic products, and applications requiring controlled conductivity or insulation.
What Standards Govern Surface Resistivity Testing?
Answer: International standards from organizations like ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) provide guidelines for surface resistivity testing methods.
How Does Surface Resistivity Affect Electrical Systems?
Answer: Understanding surface resistivity helps in selecting materials for electrical components, systems, or applications where controlled surface conductivity or insulation is essential for proper functioning and safety.