We also offer
What is Charge Decay Time
The charge decay time test evaluates how effectively a material can dissipate or eliminate electric charges over time. It measures the rate at which static electricity or electrostatic discharge (ESD) dissipates from a material’s surface after charging. This dissipation rate is a key property in applications where the buildup of static charge can affect safety, product quality, or performance.
Testing Principle and Methodology
Before testing, condition the material at 50% relative humidity for at least 12 hours. Place the material on a conducting plate, then charge its surface with approximately 5000V.
Charging is typically done through either corona discharge or triboelectrification. A static monitor tracks the charge on the surface. Once a grounding cable is applied, record how long it takes for the material to dissipate 50%, 10%, and 1% of its initial charge. Use any suitable timing device, such as a Picoscope. The charge decay is also represented graphically.
This test method applies to both powder and solid materials.
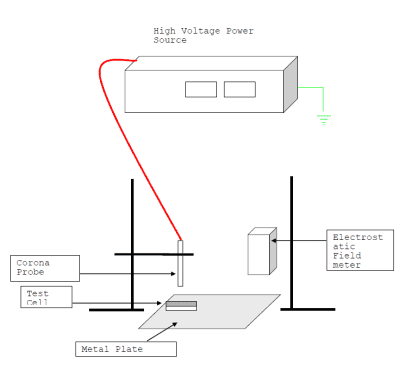
Charge Decay Time Set up
Applicable Standard
Charge relaxation time testing follows the standards below:
-
MIL-STD-3010
-
IEC-61340-4-4
-
NFPA 77
Data Interpretation
According to MIL-STD-3010, a material that relaxes its initial charge to 10% within 5 seconds is classified as static dissipative.
Knowing the charge relaxation time helps determine how to safely handle the material—such as ensuring proper earthing of equipment and personnel. This test is essential in industries like electronics, manufacturing, and packaging, where static charges can pose performance, safety, or quality risks.
When to Perform Charge Decay Time Testing
Charge decay time testing is recommended for any material prone to charge accumulation during handling or processing. The results indicate how well the material can self-dissipate static charge. Dissipative materials allow charge to migrate over their surface or through their volume in a short time. In contrast, insulating materials retain charge much longer—often undesirably so.
Why Choose Prime Process Safety Center
Prime Process Safety Center is a trusted leader in process safety testing, with highly experienced laboratory personnel. Our goal is to deliver accurate, reliable, and defensible data that meets both industry and regulatory standards.
-
We are skilled in conducting electrostatics testing, including charge decay time.
-
Our lab features state-of-the-art testing equipment for precise, sensitive measurements.
-
We follow strict protocols and quality control for consistent, reliable results.
-
Our team provides detailed analysis and recommendations tailored to your application or research needs.
- As an ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accredited laboratory, we follow rigorous quality and competency requirements for every test we perform.
FAQ
1. What is Charge Relaxation?
Answer: Charge relaxation refers to the dissipation or reduction of electric charge on a material's surface over time, typically after being charged due to static electricity or electrostatic discharge (ESD).
2. Why is Charge Relaxation Important?
Answer: Charge relaxation is crucial in assessing a material's ability to dissipate static charges, impacting product quality, safety, and functionality, especially in electronics, manufacturing, and packaging.
3. How is Charge Relaxation Tested?
Answer: Charge relaxation testing involves charging a material's surface to a known voltage and then measuring the rate at which the surface voltage decreases over a specified time to evaluate its dissipation characteristics.
4. What Factors Affect Charge Relaxation?
Answer: Material composition, surface properties, environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), and the presence of additives influence a material's ability to relax charge.
5. What Equipment is Used for Charge Relaxation Testing?
Answer: Specialized equipment such as high-impedance voltmeters or electrometers are used to measure and monitor surface charge dissipation rates over time.
6. How Does Charge Relaxation Impact ESD Control?
Answer: Understanding charge relaxation helps in designing antistatic materials or products to prevent electrostatic discharge-related damage in sensitive electronic components or manufacturing processes.
7. Where is Charge Relaxation Testing Applied?
Answer: Charge relaxation testing finds application in industries dealing with electronics, packaging, and materials susceptible to static charges that can impact product quality or performance.
8. Are There Standardized Methods for Charge Relaxation Testing?
Answer: Various organizations and standards bodies offer guidelines or testing methods to assess charge relaxation properties in materials, aiding in standardizing testing procedures.
9. What are the Implications of Charge Relaxation in Material Selection?
Answer: Materials with effective charge relaxation properties are preferred in applications requiring controlled conductivity, ESD prevention, or where static charges can affect performance.
10. How Does Charge Relaxation Testing Benefit Product Quality?
Answer: By evaluating charge relaxation, manufacturers can select materials that maintain stable electrical properties, ensuring product reliability, safety, and minimizing ESD-related risks.