We also offer
What is Liquid Conductivity Testing
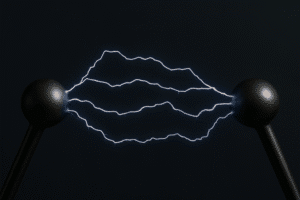
Liquid conductivity is the measurement of a fuel’s electrical resistance at the moment a DC voltage is applied between electrodes. Specifically, it measures the rest electrical conductivity—the conductivity at the initial instant of current flow—before ionic depletion or polarization occurs.
This test determines conductivity in the range of 0.1 to 2,000 picoSiemens per meter (pS/m) and is critical for evaluating electrostatic hazards. Since electrostatic charge generation and dissipation during handling depend on ionic species in the liquid, knowing the rest conductivity helps assess safety risks.
Testing Principle and Methodology
This test applies to fuel liquids. Because conductivity depends on temperature, the liquid’s temperature is measured before the test begins.
A DC voltage is applied to the outer cylindrical electrode, and a pico-ammeter measures the resulting current flowing through the sample to the inner electrode. The system records conductivity 3 seconds after applying the voltage to ensure it captures equilibrium values.
Before testing, the operator thoroughly cleans the cell with a low-conductivity liquid and flushes it several times with the test sample. To avoid contamination, they discard all wash liquids between rinses.

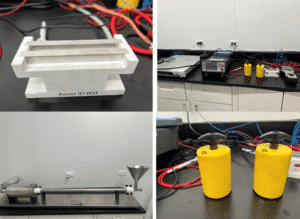
Liquid Conductivity Test Cell manufactured by Anko
Applicable Standard
The test follows ASTM D4308 – Standard Test Method for Electrical Conductivity of Liquid Hydrocarbons.
Data Interpretation
Materials are classified by conductivity into three groups:
-
Low Conductivity (< 100 pS/m): Examples include Toluene and Xylene. These insulating liquids do not easily dissipate electrostatic charges, increasing the risk of charge accumulation and potential ignition in flammable environments.
-
Medium Conductivity (100–10,000 pS/m): Includes substances like Hydrogen Sulfide. These materials allow moderate charge dissipation, reducing hazard potential.
-
High Conductivity (> 10,000 pS/m): Includes Isopropyl Alcohol and Acetone. These materials dissipate charge quickly and are less likely to accumulate hazardous static electricity.
Knowing a liquid’s conductivity class supports safe handling practices—such as grounding conductive and static-dissipative containers—based on the material’s ability to retain or dissipate charge.
When to Perform Liquid Conductivity Testing
This test is recommended when there’s a risk of a process liquid becoming electrostatically charged. It helps evaluate a liquid’s ability to accumulate and retain charge, supporting safe storage, handling, and quality control.
Conductivity testing is also used to assess a liquid’s purity, quality, and suitability for specific industrial applications.
Why Choose Prime Process Safety Center
Prime Process Safety Center offers trusted expertise in liquid conductivity testing:
-
Highly experienced laboratory staff deliver accurate, reliable, and defensible results.
-
State-of-the-art equipment ensures precise, sensitive measurements.
-
Strict testing protocols and quality controls guarantee consistency and compliance with industry standards.
- We follow rigorous quality and competency requirements for every test we perform.
-
Our experts interpret and analyze results, offering insights and recommendations tailored to your application.
We are committed to delivering data you can rely on—for compliance, safety, and peace of mind.
FAQ
What is Electrical Conductivity in Liquids?
Answer: Electrical conductivity in liquids refers to their ability to conduct electrical current. It is the result of ions or charged particles present in the liquid that allow the flow of electricity.
How is Liquid Conductivity Measured?
Answer: Liquid conductivity is measured using a conductivity meter or probe that applies a small electric current to the liquid and measures the resulting conductivity. The unit of measurement is typically picosiemens per meter (pS/m) or microsiemens per centimeter (µS/cm).
What Factors Affect Liquid Conductivity?
Answer: Various factors influence liquid conductivity, including the concentration of ions or dissolved substances, temperature, purity, and the presence of contaminants or impurities.
Why is Liquid Conductivity Testing Important?
Answer: Conductivity testing of liquids is crucial in assessing water quality, monitoring industrial processes, ensuring proper functioning of equipment, and controlling the composition of solutions in various industries such as manufacturing, environmental monitoring, and medical applications.
What Are the Applications of Liquid Conductivity Testing?
Answer: Liquid conductivity testing finds applications in water treatment, industrial processes, quality control in pharmaceuticals and food production, monitoring cooling systems, assessing wastewater, and ensuring proper functioning of various electronic and electrical systems.