We also offer
What is Chemical Reaction Hazard Assessment
Chemical Reaction Hazard Assessment is a critical component of process safety, focusing on identifying and analyzing potential hazards associated with chemical reactions in manufacturing processes. This assessment helps prevent incidents such as fires, explosions, and toxic releases, which can have severe consequences for human health, the environment, and property.
By understanding the nature and risks of chemical reactions, process safety professionals can develop strategies to manage and mitigate these hazards, ensuring the safety and reliability of industrial operations.
Steps to Conduct a Chemical Reaction Hazard Assessment
1. Identifying Potential Chemical Hazards
Chemical processes involve various reactions, some of which may be potentially hazardous.
It is important to conduct a comprehensive assessment of all chemical reactions involved in a process to identify potential hazards—not only the intended reactions but also the stability of any intermediates, including wastes. Factors such as reactivity, temperature, pressure, catalysts, and impurities must be taken into consideration.
2. Risk Evaluation and Predictive Modeling
Chemical reaction hazard assessment involves evaluating the likelihood and consequences of unwanted reactions.
Advanced predictive modeling techniques and software can simulate and analyze potential scenarios to assess the magnitude of possible hazards. Analyzing process parameters under different conditions and identifying critical points aid in determining safe operating limits for chemical processes.
3. Assessing Reaction Kinetics
Understanding the reaction kinetics is crucial for estimating reaction rates and potential heat release.
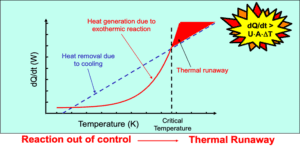
Reaction rates, along with temperature and pressure profiles, provide vital information about a reaction’s behavior. Through careful hazard assessment, potential runaway reactions or uncontrolled exotherms can be identified and mitigated proactively.
4. Thermal Stability Analysis and Calorimetry Studies
Another key aspect of a chemical reaction hazard assessment is evaluating thermal stability.
Various calorimeters (DSC, DTA, ARC, RC1, VSP, etc.) at Prime Process Safety Center allow for measurement of temperature, pressure, and heat flow as a function of time for potential failure scenarios.
By analyzing samples under different conditions, the heat flows associated with phase transitions, decomposition reactions, and exothermic events can be characterized. These insights support material compatibility studies, safe operating conditions, and effective safety design.
5. Importance of Process Design and Engineering Controls
Effective process design and engineering controls are essential for mitigating chemical reaction hazards.
By considering factors such as containment, ventilation, pressure relief, and segregation, risks associated with hazardous reactions can be minimized. Maintaining appropriate temperature, pressure, and control systems ensures stable and safe operation throughout the process.
6. Training and Procedural Safeguards
Proper training and procedural safeguards are critical for ensuring process safety.
Comprehensive operating procedures, emergency response plans, and employee training programs equip personnel with the skills to handle potential hazards safely. Ongoing safety education fosters a proactive safety culture and prevents process-related incidents.
Why Perform Chemical Reaction Hazard Assessment?
Performing a Chemical Reaction Hazard Assessment is essential for identifying and mitigating risks that could lead to accidents, injuries, or environmental harm.
Techniques such as calorimetry testing, reaction mechanism analysis, and dynamic process simulations provide a detailed understanding of process behavior and potential failure points.
These assessments support the implementation of safety measures, optimized reactor designs, accurate heat removal calculations, and prevention of overpressure or runaway conditions. Ultimately, they protect both personnel and equipment while ensuring regulatory compliance and operational reliability.
Why Choose Prime Process Safety Center
Expertise: Our experienced professionals specialize in chemical reaction hazard assessment, providing deep insight into evaluating and mitigating chemical risks.
Customized Approach: Each process is unique. We tailor our assessments to your specific operational needs and go beyond standard protocols to develop custom safety strategies.
Comprehensive Analysis: Using advanced analytical techniques and software, we evaluate reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, reaction pathways, and reactivity hazards for a thorough understanding of risks.
Cost-Effective Solutions: We offer practical, cost-efficient safety solutions that balance safety and productivity while minimizing operational disruption.
Ongoing Support: We provide continuous support through training, reviews, and implementation guidance to help maintain safe and compliant operations.
Partnering with Prime Process Safety Center gives you access to expert insight, customized safety planning, and ongoing technical support for a safer, compliant, and more efficient operation.
FAQ
1. What is chemical reaction hazard assessment?
Chemical reaction hazard assessment is the systematic evaluation and identification of potential hazards and risks associated with chemical reactions in order to prevent accidents and ensure safety in industrial and laboratory settings.
2. Why is chemical reaction hazard assessment important?
Chemical reaction hazard assessment is important because it helps identify and understand the potential risks and hazards associated with chemical reactions, allowing for the implementation of appropriate safety measures to prevent accidents, injuries, and damages.
3. What are the potential risks associated with chemical reactions?
Potential risks associated with chemical reactions include fire, explosion, release of toxic gases or substances, thermal runaway, over-pressurization, formation of reactive intermediates, and uncontrolled reactions leading to loss of containment.
4. How is a chemical reaction hazard assessment conducted?
A chemical reaction hazard assessment involves reviewing the properties of the chemicals involved, assessing potential reaction conditions, analyzing reaction pathways, conducting thermal analysis, and considering factors such as concentration, temperature, pressure, and compatibility.
5. What factors are considered during a chemical reaction hazard assessment?
Factors considered during a chemical reaction hazard assessment include the nature of the chemicals involved, reaction conditions (e.g., temperature, pressure, pH), potential reaction pathways, reactivity hazards, compatibility, exposure routes, and potential consequences.
6. What are some common reactive hazards that may be identified during an assessment?
Common reactive hazards that may be identified during a chemical reaction hazard assessment include exothermic reactions, overpressure, too short of time to maximum rate (TMR), reactive control problems, incompatibilities (e.g., mixing incompatible chemicals), polymerization reactions, and reactions involving hazardous materials (e.g., heavy metals).
7. How can a chemical reaction hazard assessment help prevent accidents and injuries?
Chemical reaction hazard assessments help prevent accidents and injuries by identifying potential risks and hazards, allowing for the implementation of appropriate control measures such as process modifications, equipment design improvements, use of protective equipment, and emergency response planning.
8. Can a chemical reaction hazard assessment help with regulatory compliance?
Yes, chemical reaction hazard assessments play a critical role in ensuring regulatory compliance. Many regulatory bodies require companies to conduct hazard assessments to assess and mitigate the risks associated with chemical reactions.
9. How often should a chemical reaction hazard assessment be conducted?
The frequency of chemical reaction hazard assessments depends on several factors, including the nature of the chemical processes, changes in processes or equipment, new chemical introductions, and regulatory requirements. Generally, assessments should be done regularly and whenever there are significant changes.
10. What are some recommended mitigation strategies for identified reaction hazards?
Mitigation strategies for identified reaction hazards may include process modifications, use of inherently safer alternatives, implementation of engineering controls (e.g., containment systems), proper storage and handling practices, effective labeling and signage, training and education programs, and emergency response planning.