We also offer
What is Reaction Calorimetry?
Reaction calorimetry is a key technique in chemical engineering and research used to measure the heat released or absorbed during chemical reactions. This method provides critical insights into reaction thermodynamics, supporting studies in reaction kinetics, process safety, and optimization. By accurately tracking heat flow, reaction calorimetry helps characterize the energetics of chemical transformations and assess potential hazards.
Principle of Operation
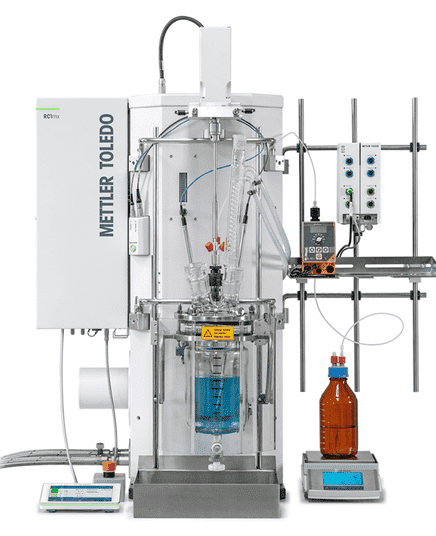
A reaction calorimeter (RC) replicates real plant operating conditions during a reaction. It can operate in either isothermal mode or temperature-programmed mode. Like an industrial stirred tank reactor, an RC allows for controlled reactant addition, refluxing, distillation, and other operations while monitoring heat flow and related thermal phenomena.
Because of these capabilities, RCs are widely used for:
-
Safety analysis
-
Process development
-
Scale-up studies
Data Interpretation
Reaction calorimetry generates several types of data, including temperature, heat flow, and pressure or gas generation over time.
Key interpretations include:
-
Heat of reaction – calculated by comparing calibration curves with reaction curves and normalizing to the limiting reagent.
-
Adiabatic temperature rise – determined using heat capacity values.
-
Accumulation level – percentage of unreacted material present when feeding stops.
-
Exothermic activity – detection of continued reaction after reagent addition.
-
Physical changes – such as color shifts or viscosity changes.
-
Gas generation – measured with accessory equipment.
-
Intermediate tracking – using accessories like FTIR detectors.
From these analyses, you can determine:
-
Heat of the intended reaction
-
Adiabatic temperature rise
-
Extent of accumulation
-
Power output vs. time
-
Gas generation and intermediate behavior
Why Perform Reaction Calorimetry Test?
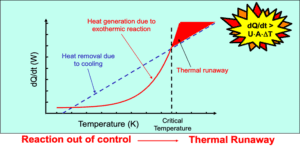
Reaction calorimetry is essential for process safety because it measures the heat generation and potential hazards associated with chemical reactions. By monitoring heat release rates and temperature changes, RC testing helps identify exothermic reactions that could lead to:
-
Thermal runaway
-
Uncontrolled reactions
-
Explosions
The data gained from RC tests support:
-
Safer process design and optimization
-
Evaluation of different reaction scenarios
-
Selection of effective control strategies to minimize risks
Through accurate measurement and analysis, reaction calorimetry ensures safer and more efficient operations, reducing hazards for personnel, facilities, and the environment.
Why Choose Prime Process Safety Center
-
Expertise you can trust – Our team has extensive experience in reaction calorimetry testing, ensuring accurate and reliable results.
- Accreditation: Testing performed in our ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accredited laboratory.
-
Thorough analysis – We provide detailed interpretation of your test data, giving you valuable insights into material behavior, stability, and hazards.
-
Efficient and cost-effective – Outsourcing your RC testing to our specialists saves time and resources.
-
Tailored reporting – We deliver comprehensive reports and practical recommendations designed to meet your specific needs and objectives.
FAQ
1. What is reaction calorimetry?
Reaction calorimetry is a technique used to measure the heat generated or consumed during a chemical reaction. It provides valuable information about the thermal behavior and safety hazards of reactions, helping in the optimization of process conditions and the assessment of potential risks.
2. Why is reaction calorimetry important in process safety?
Reaction calorimetry plays a crucial role in process safety by providing insights into the thermal behavior of reactions. It helps to identify and mitigate potential hazards associated with exothermic reactions, such as runaway reactions or thermal explosions. By understanding the heat release and heat transfer during reactions, process engineers can design safer and more efficient processes.
3. How is reaction calorimetry performed?
Reaction calorimetry involves conducting experiments in specialized calorimeters designed to measure heat effects. Typically, reactants are mixed in a calorimeter, and the heat generated or consumed is measured through temperature changes. Data obtained from these experiments can be used to calculate heat transfer coefficients, heat capacity, reaction kinetics, and other parameters relevant to process safety.
4. What are the benefits of using reaction calorimetry in process safety studies?
Using reaction calorimetry in process safety studies provides several advantages. It allows for the early identification of hazardous reactions, facilitates the optimization of reaction conditions to enhance safety, and provides data necessary for the design of safe operating processes.
5. Can reaction calorimetry be used for scale-up purposes?
Yes, reaction calorimetry data can be used for scale-up purposes. By understanding the heat generation or consumption behavior of reactions at a small scale, it is possible to predict and control the thermal behavior when scaling up to larger production volumes. This helps in ensuring the safety and efficiency of the process at different scales, minimizing the risks associated with large-scale reaction.