We also offer
What is Autoignition Temperature (AIT) Testing
The autoignition temperature (AIT) is the minimum temperature at which the vapor of a liquid or gas ignites spontaneously from environmental heat—without an external ignition source such as a spark or flame. AIT is the point where air oxidation alone causes ignition.
Autoignition temperature depends on both the chemical and physical properties of the material and the test method used. Factors influencing AIT include ignition delay, vapor concentration, test volume, pressure, oxygen content, and catalytic effects.
While this test is primarily performed on gases, it can also be used for liquids and solids capable of full vaporization.
Testing Principle and Methodology
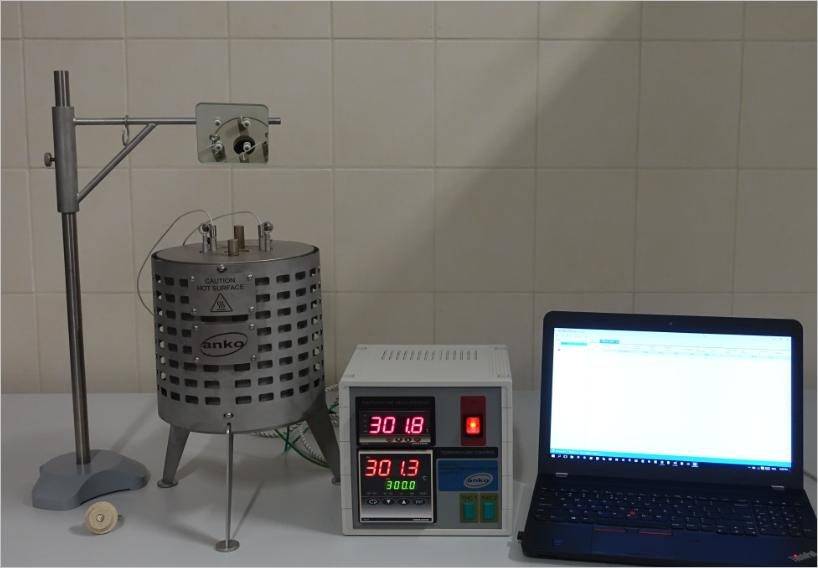
The process begins by preparing different concentrations of the material. A selected volume, typically 100 μL, is injected into a heated and thermally stabilized 500 mL round-bottom flask using a hypodermic syringe.
-
If ignition occurs, the flask temperature is reduced, and the concentration is adjusted until the AIT is identified.
-
If ignition does not occur within 10 minutes, the temperature is increased in 30°C increments, with concentration adjustments after each step.
-
Testing continues until the difference between ignition and non-ignition temperatures is 3°C.
Applicable Standard
Testing follows ASTM E659 – Standard Test Method for Autoignition Temperature of Chemicals.
Data Interpretation
AIT data is critical for determining the maximum permitted surface temperature of electrical and non-electrical equipment in areas where the tested material may be present. This ensures correct classification of equipment according to its temperature or “T” Class.
Example AIT values for common flammable liquids:
-
Acetic acid: 175°C
-
Benzene: 298°C
-
Diethylamine: 312°C
-
Diethyl ether: 160°C
-
Ethyl acetate: 410°C
When to Perform Autoignition Temperature (AIT) Testing
AIT testing is essential in several scenarios to evaluate the risk of spontaneous ignition without an external spark or flame. Situations where this test is recommended include:
-
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) preparation – Many industries require accurate AIT values for chemical SDS documentation.
-
Safe handling and storage – Knowing the AIT helps define operational limits and storage parameters to prevent ignition.
-
Material selection – AIT data ensures chosen materials won’t spontaneously ignite under expected operating conditions.
-
Regulatory compliance – Safety standards and regulations often mandate AIT testing for chemicals used in industrial applications.
Why Choose Prime Process Safety Center
At Prime Process Safety Center, we specialize in accurate, reliable, and defensible process safety testing that meets industry and regulatory standards.
-
Experienced laboratory personnel – Our team has extensive expertise in autoignition temperature testing.
-
State-of-the-art equipment – We use advanced, precise, and sensitive AIT testing instruments.
-
Strict quality control – All tests follow rigorous protocols to ensure repeatable and reliable results.
- Accreditation – Testing performed in our ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accredited laboratory, ensuring recognized competency and adherence to international quality standards.
-
Expert analysis and insights – We interpret and analyze AIT data, providing recommendations tailored to your application or research.
FAQ
What is Autoignition Temperature?
Answer: Autoignition temperature refers to the lowest temperature at which a substance spontaneously ignites without an external ignition source or flame, simply due to the heat of the material itself.
Why is Autoignition Temperature Important?
Answer: Knowing the autoignition temperature of a substance is crucial for understanding its potential fire hazards, determining safe handling and storage conditions, and ensuring workplace safety.
How is Autoignition Temperature Determined?
Answer: Autoignition temperature is determined through standardized laboratory testing methods. Common techniques include heating the substance in a controlled environment and observing at what temperature it ignites.
What Factors Influence Autoignition Temperature?
Answer: Various factors affect the autoignition temperature, such as the chemical composition of the substance, pressure, presence of impurities, and environmental conditions like humidity.
How is Autoignition Temperature Used in Industry?
Answer: Autoignition temperature data is utilized in industry for risk assessment, safety protocol development, material selection, storage and handling guidelines, and compliance with safety regulations.