We also offer
What Is Process Safety Management (PSM)?
Process Safety Management (PSM) is a structured framework designed to manage the risks associated with highly hazardous chemicals and processes. Its primary goal is to prevent catastrophic events such as explosions, fires, toxic releases, and other major process incidents.
PSM is especially critical for industries like:
-
Chemical manufacturing
-
Oil and gas production
-
Petrochemical refineries
-
Pharmaceutical plants
-
Facilities handling flammable or toxic chemicals
In the United States, PSM is legally required under OSHA’s Process Safety Management standard (29 CFR 1910.119). Other countries have similar regulations and guidelines to manage chemical process safety.
Why Is Process Safety Management (PSM) Important?
Implementing a strong PSM program helps organizations:
-
Prevent fires, explosions, and hazardous chemical releases
-
Protect workers, surrounding communities, and the environment
-
Comply with OSHA and other safety regulations
-
Maintain operational continuity and reduce costly downtime
-
Foster a proactive safety culture and reduce legal liability
By identifying risks and putting controls in place, PSM enables safer and more reliable operations for high-hazard industries.
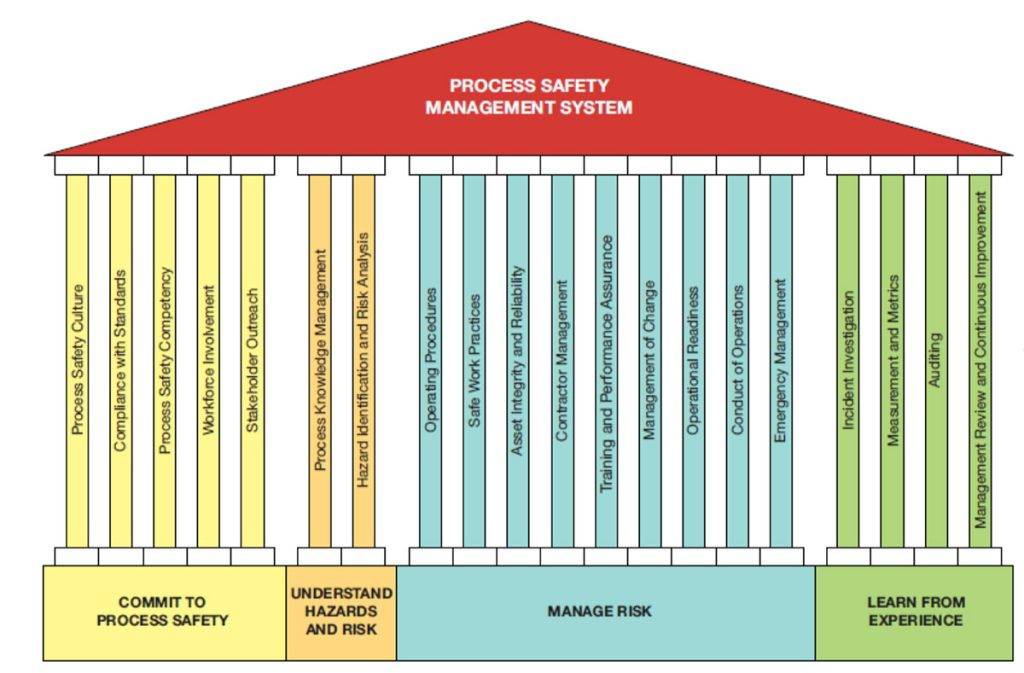
Key Elements of a Process Safety Management Program
An effective PSM program includes the following core components:
1. Process Hazard Analysis (PHA)
Evaluate potential hazards using tools like HAZOP, What-If analysis, and checklists.
2. Process Safety Information (PSI)
Maintain detailed records of equipment specs, process diagrams, operating limits, and Safety Data Sheets (SDS).
3. Operating Procedures
Create clear instructions for startup, normal operation, shutdown, and emergencies. Regularly review and update them.
4. Employee Training
Train all employees and contractors on safety protocols, process hazards, and emergency actions.
5. Mechanical Integrity
Regularly inspect and maintain equipment (valves, pumps, vessels, etc.) to prevent failures.
6. Management of Change (MOC)
Assess the safety impact of changes to equipment, processes, personnel, or materials before implementing them.
7. Pre-Startup Safety Review (PSSR)
Conduct a thorough safety check before introducing new processes or restarting after major changes.
8. Emergency Planning and Response
Develop and practice evacuation plans, fire response, spill containment, and communication procedures.
9. Incident Investigation
Analyze incidents and near misses to identify root causes and prevent recurrence.
10. Compliance Audits
Perform regular audits to assess the effectiveness of your PSM program and ensure regulatory compliance.
11. Hot Work Permit
Issue permits for welding, cutting, or other high-heat tasks to ensure ignition sources are properly controlled.
12. Contractor Safety
Verify that third-party contractors follow your site-specific safety rules and are trained on hazards.
13. Trade Secrets Access
Ensure employees have access to critical safety information, even if it’s proprietary.
14. Employee Participation
Involve staff at all levels in developing, implementing, and improving the PSM program.
Why You Need PSM in Your Facility
Whether you’re handling flammable liquids, toxic gases, or high-pressure processes, PSM provides:
-
Risk visibility and mitigation
-
Stronger emergency readiness
-
Regulatory compliance (OSHA, EPA, etc.)
-
Protection for employees and assets
-
Operational resilience and public trust
Neglecting PSM can result in severe consequences, from legal fines to environmental disasters.
Why Choose Prime Process Safety Center
At Prime Process Safety Center, we offer end-to-end PSM services tailored to your facility’s operations, risks, and regulatory requirements.
What Sets Us Apart:
- Expertise in OSHA PSM standards and global safety regulations
- Custom PSM strategies aligned with your industry and operations
- Risk identification and mitigation support at every level
- Employee training and empowerment to build a safety-first culture
- Comprehensive documentation and reporting for audits and regulators
- Ongoing program updates as your business evolves
- Incident investigation and analysis services to improve prevention
- Long-term partnership approach to maintain high safety performance
FAQ
1. What is Process Safety Management (PSM)?
PSM is a regulatory framework aimed at preventing accidents, injuries, and incidents in industries that handle hazardous chemicals by managing the integrity of processes.
2. Why is PSM important in industrial settings?
PSM is crucial for ensuring the safe operation of facilities that use hazardous chemicals, thereby protecting employees, the environment, and the public from potential accidents like fires, explosions, and toxic releases.
3. What industries require PSM implementation?
PSM is typically required in industries like chemical manufacturing, oil refining, gas processing, and any other sector where hazardous chemicals are processed or stored.
4. What are the key elements of PSM?
PSM includes elements such as process hazard analysis, operating procedures, mechanical integrity, management of change, employee training, and emergency planning and response.
5. How does PSM differ from Occupational Safety and Health (OSH)?
While OSH focuses on general workplace safety and health issues, PSM specifically addresses the unique risks associated with processing hazardous chemicals.
6. What role does employee training play in PSM?
Training ensures that employees understand the processes they work with, recognize potential hazards, and know how to respond in emergencies, making it a critical aspect of PSM.
7. How often should a process hazard analysis (PHA) be conducted?
OSHA recommends conducting a PHA every five years or when significant changes to a process occur.
8. What is Management of Change in PSM?
Management of Change is a systematic approach to managing safety implications of changes in processes, equipment, personnel, or materials in a facility.
9. How is compliance with PSM regulations enforced?
Regulatory bodies like OSHA enforce PSM compliance through inspections, audits, and penalties for non-compliance.
10. What are the regulatory requirements for Process Safety Management (PSM)?
The regulatory requirements for Process Safety Management (PSM) primarily stem from the standards set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States, specifically in the OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.119. This standard is designed to prevent or minimize the consequences of catastrophic releases of toxic, reactive, flammable, or explosive chemicals. These requirements apply to industries that deal with hazardous chemicals, including but not limited to petroleum refineries, chemical plants, and other industrial facilities.