We also offer
What Is Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA)?
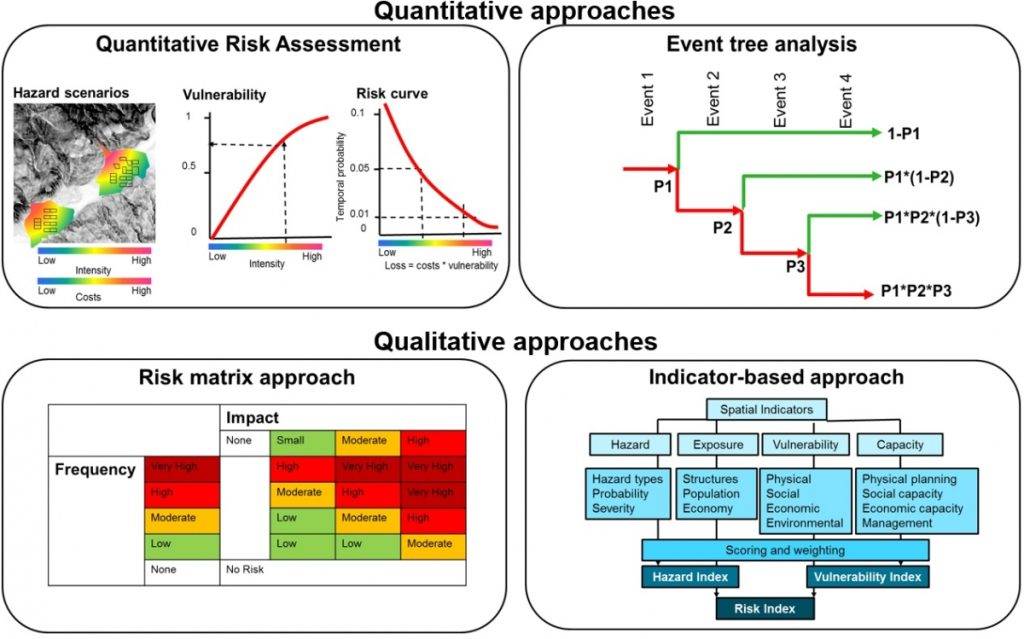
Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA) is a structured and data-driven method used to identify and evaluate the risks associated with industrial processes. It calculates both the likelihood and consequences of hazardous events, offering a numerical estimation of risk. QRA is especially vital in high-risk industries like chemical manufacturing, oil and gas, and pharmaceuticals, where failures can result in serious harm to people, the environment, and assets.
Using historical incident data, statistical analysis, and probabilistic models, QRA helps quantify the frequency and impact of potential events such as fires, explosions, toxic releases, or equipment failures. This measurable approach allows for objective, evidence-based decision-making and more effective risk management.
Why Perform a Quantitative Risk Assessment?
QRA provides a range of benefits for organizations committed to process safety and compliance:
-
Quantifies risk: Assigns numerical values to the probability and severity of incidents
-
Improves decision-making: Helps prioritize risk mitigation based on highest threats
-
Enhances communication: Simplifies complex risk scenarios for stakeholders, regulators, and teams
-
Supports regulatory compliance: Demonstrates due diligence under safety regulations (e.g., OSHA, EPA)
-
Guides resource allocation: Focuses investments where risk is greatest
-
Improves emergency planning: Identifies worst-case scenarios and informs response strategies
-
Drives continuous improvement: Offers insights for process optimization and long-term safety planning
How Is Quantitative Risk Assessment Conducted?
Implementing a QRA involves the following key steps:
-
Hazard Identification
Identify potential risks like chemical leaks, fires, explosions, and operational errors. -
Scenario Development
Create credible scenarios outlining how each hazard could lead to a hazardous event. -
Frequency Analysis
Estimate how often these scenarios may occur using historical data and probabilistic models. -
Consequence Analysis
Evaluate the physical and human impact—such as toxic dispersion, structural damage, or injury. -
Risk Calculation
Combine frequency and consequence data to generate quantitative risk values. -
Define Risk Criteria
Set acceptable risk thresholds based on internal policies and regulatory standards. -
Risk Comparison
Identify gaps by comparing calculated risks to acceptable levels. -
Develop Mitigation Strategies
Recommend control measures to lower risk through prevention or impact reduction. -
Implement Controls
Apply engineering, administrative, or procedural safeguards, and update emergency response plans. -
Documentation & Reporting
Record all findings for compliance, internal use, and stakeholder communication. -
Review & Update
Regularly update the QRA as processes, technologies, or regulations change. -
Stakeholder Engagement
Involve operations, safety, engineering, and management teams throughout the process.
Why Choose Prime Process Safety Center
At Prime Process Safety Center, we bring deep experience and technical skill to every QRA project. Here’s what sets us apart:
-
Specialized Expertise
Our team has extensive experience in risk analysis across diverse process industries. -
Advanced Methods & Tools
We use state-of-the-art statistical models and risk software for precise assessments. -
Tailored Solutions
Every QRA is customized to your site’s operations, hazards, and business goals. -
End-to-End Support
From hazard identification to implementation of controls, we’re with you every step of the way. -
Compliance Assurance
We help you meet regulatory requirements and prepare for audits with confidence. -
Effective Communication
Our reports are clear, actionable, and stakeholder-ready—ideal for decision-making and training. -
Risk Mitigation Strategy
We go beyond assessment to offer actionable solutions for reducing both frequency and impact. -
Training & Facilitation
We provide Facilitation and Scribing Personnel to support documentation, knowledge transfer, and team empowerment. -
Continuous Improvement Focus
We offer ongoing updates, risk reassessments, and strategy refinement to adapt to changes in your operations.
FAQ
1. What is Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA)?
QRA is a methodical approach used in the process industry to quantify the likelihood and potential impact of hazardous events, providing a numerical basis for risk evaluation.
2. Why is QRA important in the process industry?
QRA is vital for identifying, quantifying, and managing risks in complex industrial settings, facilitating informed decision-making to enhance safety and operational efficiency.
3. How does QRA differ from qualitative risk assessments?
Unlike qualitative assessments, QRA provides specific numerical values for risk, offering a more objective and measurable approach to risk analysis.
4. What are the key components of QRA?
Key components include hazard identification, scenario development, frequency analysis, consequence analysis, and risk calculation.
5. How is the frequency of an event calculated in QRA?
Frequency is calculated using statistical data, historical incident records, and probabilistic models to estimate the likelihood of an event occurring.
6. What types of risks can QRA assess in the process industry?
QRA can assess a wide range of risks, including equipment failures, operational errors, fire, explosions, toxic releases, and environmental impacts.
7. Who should be involved in conducting a QRA?
A multidisciplinary team including safety engineers, process engineers, and risk management professionals should be involved for comprehensive analysis.
8. How are the results of QRA used in the process industry?
Results are used for prioritizing risk control measures, improving safety management, informing emergency response planning, and aiding compliance with regulations.
9. What challenges are associated with QRA?
Challenges include the need for accurate data, complexity of probabilistic modeling, and ensuring the comprehensiveness of risk scenarios.
10. Can QRA results be used for regulatory compliance?
Yes, QRA results are often used to demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and safety standards, providing a robust basis for safety case submissions.